What is an LED?
An LED (Light-Emitting Diode) is an electronics component that emits light when it is powered. Since it is a diode, and diodes only let the current flow in one direction, an LED must be wired correctly for it to work.
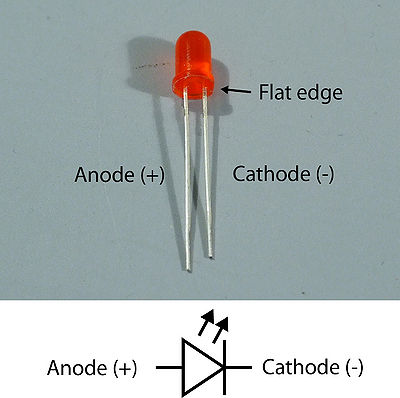
When connecting an LED it is important to be able to distinguish which lead is the anode (positive) and which is the cathode (negative). To make it easier to identify the leads, all LEDs are manufactured with two physical properties. The first is that LEDs have one lead that is longer that the other. This longer lead is the anode (+), and the shorter one is the cathode (-). The second feature is a small flat notch on the side of the LED. The lead that is closer to the notch is always the cathode. This is important to remember since the leads may have been clipped.
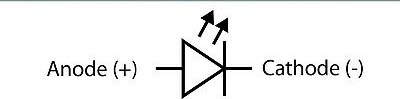
When referencing a schematic (drawing of the electrical pathways and components using symbols), the symbol for the LED shows which way the current flows and allows you to connect the LED the correct way. The cathode on the symbol is the side with the line across the point of the triangle and the anode is the other side. It is important to note that there are many variations on the schematic symbol, however, they all have a triangle with a line across the point and one or two arrows pointing out.
 What is an LED and how to use one
What is an LED and how to use one